Bacterial Infections of the Skin
Bacterial Infections of the Skin: Types, Symptoms, and Treatment
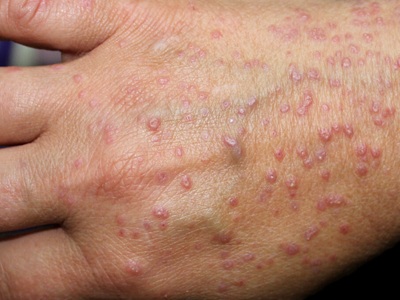
Bacterial infections of the skin are common conditions that can present with redness, swelling, pain, and other symptoms. These infections often occur when bacteria enter the skin through cuts, wounds, or other openings. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent the infection from spreading and to maintain skin health.
Types of Bacterial Skin Infections
-
Cellulitis
- What is it?: A bacterial infection affecting the deeper layers of the skin, usually caused by streptococcus or staphylococcus bacteria.
- Symptoms: Redness, swelling, warmth, pain, and sometimes fever.
- Treatment: Treated with oral or intravenous antibiotics.
-
Impetigo
- What is it?: A highly contagious, superficial skin infection, often seen in children.
- Symptoms: Yellowish crusted sores or blisters.
- Treatment: Topical antibiotic creams or oral antibiotics.
-
Folliculitis
- What is it?: Infection or inflammation of the hair follicles.
- Symptoms: Small, red, or white-headed bumps around hair follicles.
- Treatment: Antibacterial soaps, topical antibiotics, or oral antibiotics if severe.
-
Furuncles and Carbuncles
- What is it?: Larger abscesses caused by infected hair follicles; multiple furuncles can merge to form a carbuncle.
- Symptoms: Painful, red, pus-filled swellings.
- Treatment: Surgical drainage and antibiotics.
-
Erythrasma
- What is it?: A superficial infection caused by Corynebacterium minutissimum.
- Symptoms: Brownish or reddish patches, often in the armpits, groin, or skin folds.
- Treatment: Topical antibiotics and antibacterial soaps.
Symptoms of Bacterial Skin Infections
- Redness and swelling of the skin
- Pain and tenderness in the affected area
- Fluid-filled blisters or pus-filled bumps
- Warmth in the infected area
- Fever, fatigue, and swollen lymph nodes in severe cases
Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase the risk of bacterial skin infections:
- Cuts, scrapes, or wounds on the skin
- Weakened immune system
- Chronic conditions such as diabetes
- Poor hygiene
- Close contact transmission
Treatment Options
-
Antibiotic Therapy
- Topical antibiotics (creams or ointments) are sufficient for mild infections.
- Oral or intravenous antibiotics are used for more severe infections.
-
Surgical Intervention
- Drainage of abscesses is necessary for large or deep infections.
-
Supportive Care
- Antiseptic soaps and proper hygiene help prevent the spread of infection.
Preventing Bacterial Skin Infections
- Clean Wounds Promptly: Clean and cover cuts and wounds immediately.
- Practice Good Hygiene: Regularly bathe and keep your skin clean.
- Avoid Sharing Personal Items: Do not share towels, razors, or other personal items.
- Boost Immunity: Support your immune system with a healthy diet, exercise, and adequate sleep.
Conclusion
Bacterial infections of the skin can be effectively managed with early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. If you notice symptoms like redness, swelling, or pain, consult a dermatologist to prevent the infection from worsening or spreading.
For professional care and guidance, contact our clinic and take the first step toward healthier skin!