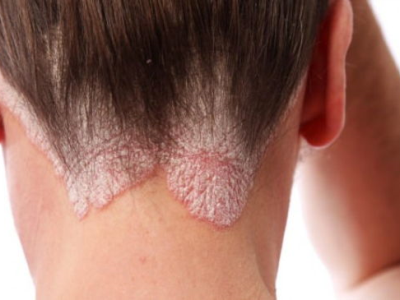
What is eczema? How do I know if it is allergic or due to irritation?
eczema is a skin disease that begins with redness and crusting, sometimes accompanied by oozing and itching. It is quite common in the community and can be seen from childhood and infancy.
Eczema can be acute but often recurs and may become chronic. In cases of chronic eczema, which lasts more than three weeks and recurs, underlying allergic or irritant conditions should be investigated. For allergic eczema, we recommend a patch test. This test checks for reactions to about 30 standard allergens, such as latex, lanolin, nickel, and neomycin, that do not cause disease in the normal population. Those who react to these substances should try to avoid them, as repeated exposure will lead to eczema flare-ups. The fundamental clinical difference of allergic eczema is that it can cause severe reactions that spread throughout the body, not just at the site of contact.
Irritant contact dermatitis, or irritant eczema, can be observed in any individual exposed to irritating agents for a prolonged period. It typically occurs after chronic exposure to chemicals such as soap, detergents, cement, and paint. Occupational diseases often fall into this category. We can observe irritant dermatitis in meticulous homemakers or individuals who frequently wash their hands. It is a more localized condition, commonly seen only in areas that have come into contact with the irritating agent. The recurrence can be prevented by using protective clothing and gloves.